The Waning Gibbous is an intermediary Moon phase. It starts right after the Full Moon, and it lasts until the Third Quarter.
When the Moon is in the Waning Gibbous phase, the sunlit part of the Moon is decreasing from 99.9% to 50.1%.
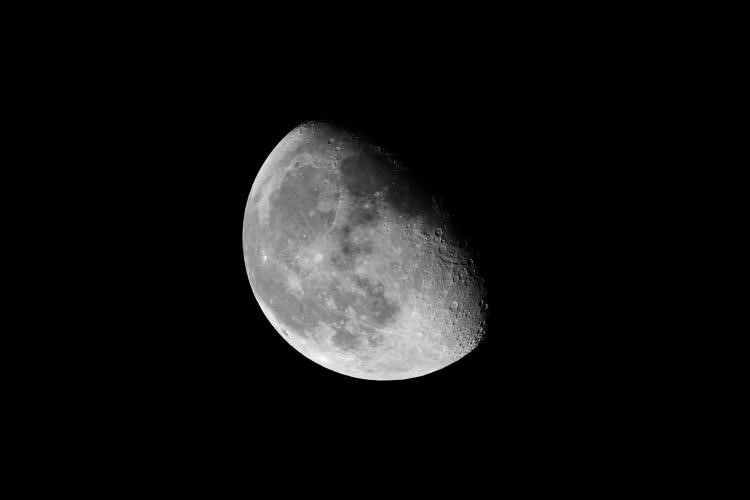

Let's find out more about this phase of the Moon and how it affects us.
What Does a Waning Gibbous Moon Look Like?
In the Waning gibbous phase, you can see the Moon late at night or in the early morning. Its illumination is less than full but more than 50%. In some cases, it may appear red like a full moon, but usually, it looks like a misshapen replica of a Full Moon.
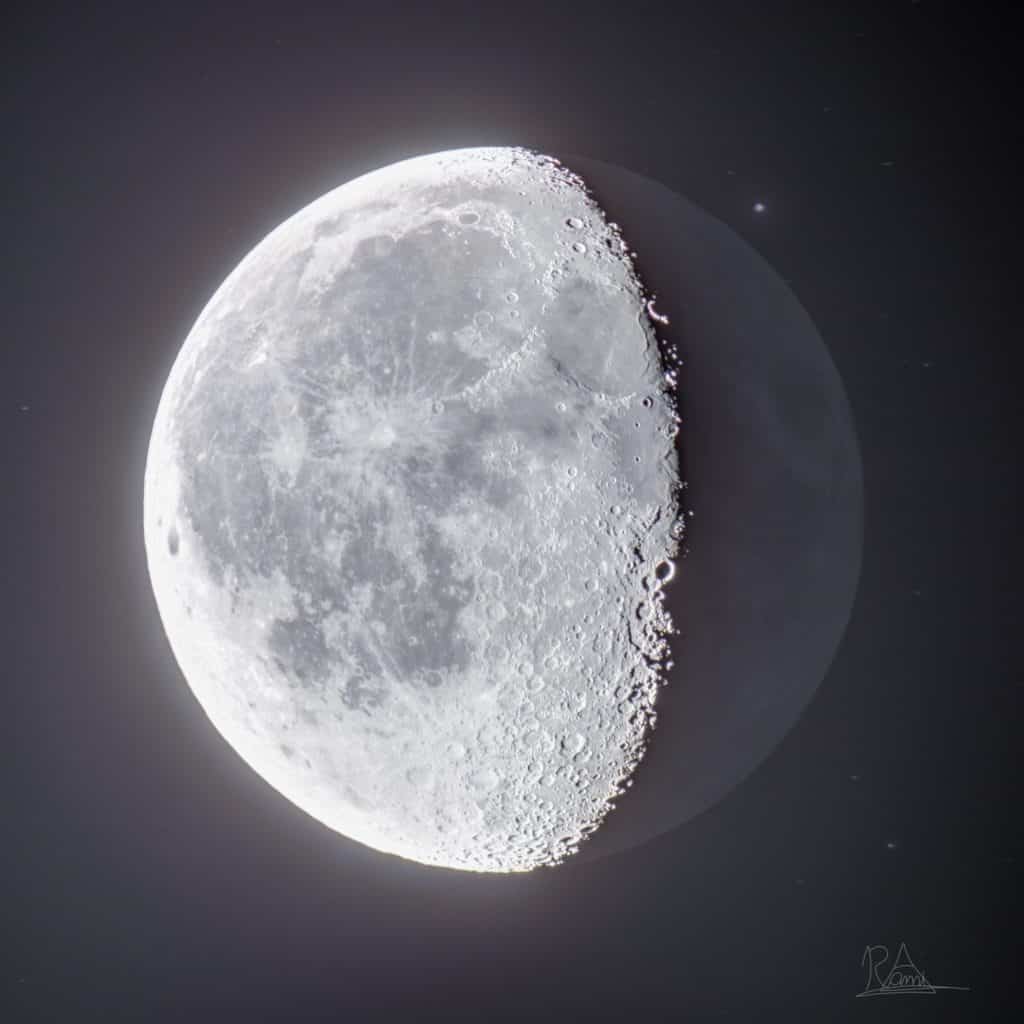

What Are the 8 Phases of the Moon?
The Moon's phases are divided into eight descriptions for a better understanding. They represent the amount of illuminated part of the Moon we can see from the Earth.
The New Moon: The New Moon occurs when the Earth, Moon, and the Sun are aligned with the Moon in the middle. So, the Sun illuminates half of the Moon we cannot see.
The Full Moon: The Full Moon - The Moon, Earth, and Sun are almost aligned, but the Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth so that we can see the entire sunlit part of it.
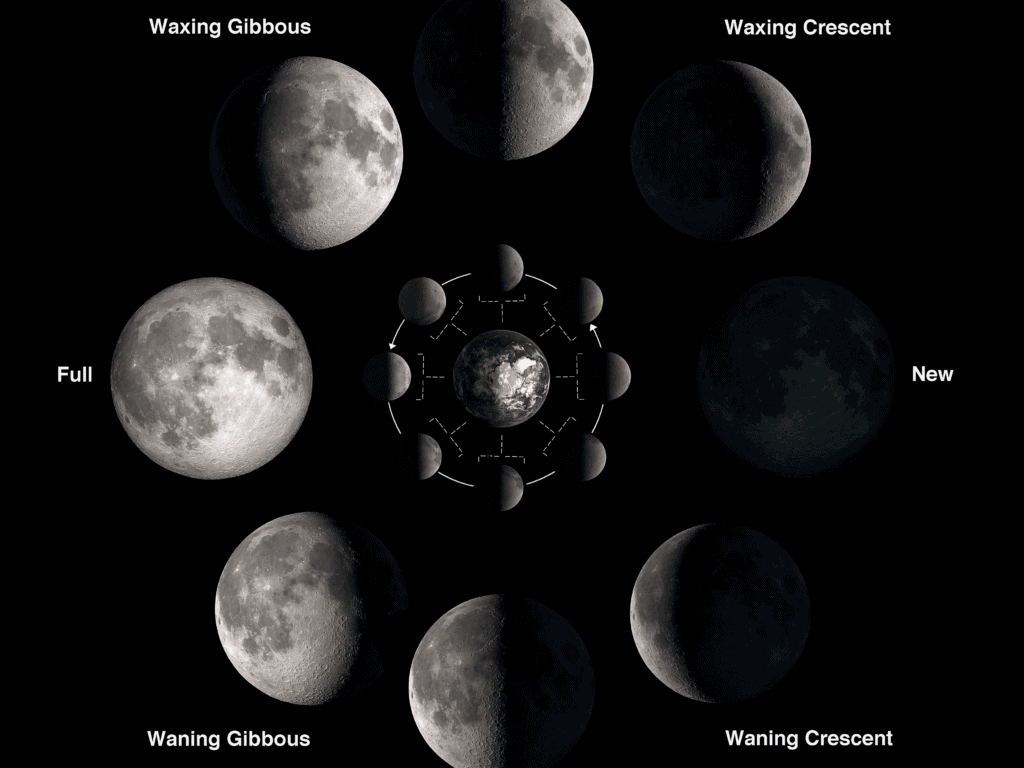
The First and Third Quarter: The First Quarter and the Third Quarter are when we can see half of the illuminated part and half of the Moon's shadow part. This is why generally, these phases are known as Half Moon. We can only see half and half because the Moon is at a 90-degree angle with respect to the Earth and Sun.
The Waxing Crescent phase: The Moon is Waxing crescent after the new Moon when the sunlit part increases, but less than a half.
The Waxing Gibbous phase: The Waxing gibbous is when the sunlit part of the Moon is now more than a half and still increasing.
The Waning Gibbous phase: After the maximum phase of a Full Moon, the light starts decreasing, which is why it is called the Waning gibbous phase. This phase lasts until the Third Quarter.
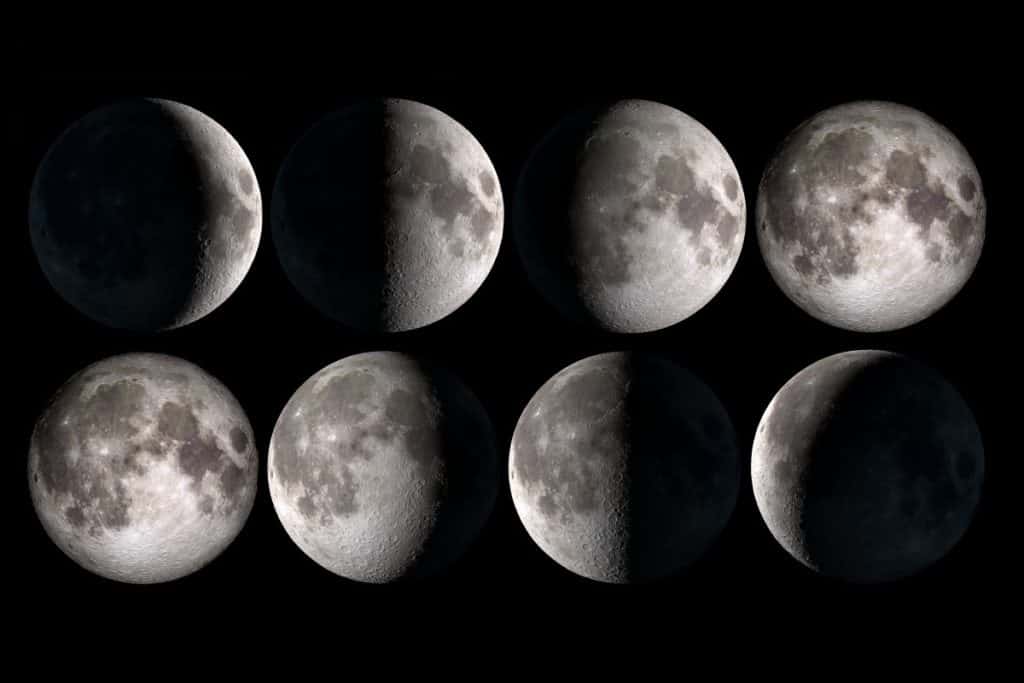

The Waning Crescent Phase: Following the Third Quarter, lights wane until the New Moon, when it's completely gone. This is the Waning crescent phase.
What is the Moon phase today? Find out here. If you are curious about the Moon phase of tomorrow, check this out. What was the Moon's phase yesterday? Find out here.
How Does a Waning Gibbous Occur?
After the Full Moon, the light will start to decrease again. Until the illuminated part of the Moon reaches 50%, it's called the Waning gibbous phase. It occurs between a Full and a New Moon.
What Does A Waning Moon Symbolize?
The Waning Gibbous phase of the Moon is the perfect time in the month to be grateful and share the right thing you have in life with the loved ones. The light of the Moon is starting to decrease until a New Moon, and it means you can now benefit from the hard work you had to do for the last two weeks.
It is the time of the month when you should finish all your projects and start cleaning your mental space.
What Does Waning Mean?
Waning means a gradual decrease of the sunlit part of the Moon after the Full Moon. The waning process lasts until the New Moon. It has two phases: the waning gibbous (when the illumination decreases to 50%) and the waning crescent ( the illumination drops to just 2%).
How Do You Tell if the Moon is Waxing or Waning?
It's not very hard to distinguish the waning Moon from the waxing Moon. It doesn't matter where you live on Earth. If you look after the Moon at sunset and you can see it, it means the Moon it's waxing.
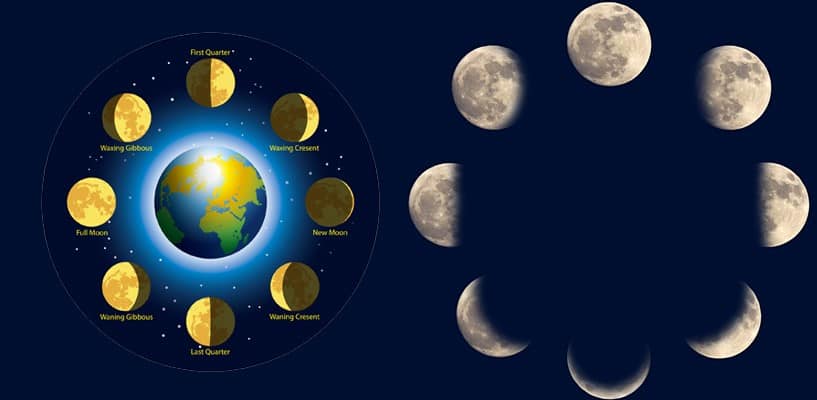
In its waning phase, the Moon isn't visible at sunset. It rises later in the night until it reaches the waning crescent phase.
When the Moon is waxing in the Northern Hemisphere, the part in the shadow will be on the left. When the shadow part is on the right, the Moon is waning. For the Southern Hemisphere, the situation is reversed.
What Comes First Waning or Waxing?
If we consider the New Moon, the first primary phase of the Moon, then the Waning phase comes first. After the New Moon, it enters the waning crescent phase, followed by the Third Quarter and the Waning Gibbous.
The Waxing Gibbous comes right next after the Full Moon. The Waxing Crescent is the last phase until the Moon reaches its New Moon phase again.
Waning Gibbous calendar for 2020
If you wonder when you can gaze at the Waning Gibbous phase in 2020, here's a list with all the dates:
- January: From the 12th until the 15th
- February: From the 11th until the 14th
- March: From the 11th until the 14th
- April: From the 9th until the 12th
- May: From the 9th until the 12th
- June: From the 7th until the 11th
- July: From the 7th until the 10th
- August: From the 5th until the 9th
- September: From the 4th until the 8th
- October: From the 4th until the 7th
- November: From the 2nd until the 6th
- December: From the 2nd until the 6th
Waning Gibbous calendar for 2021
The Waning Gibbous phase of the Moon happens every month. Let's find out the dates:
- January: From the 1st until the 4th and from the 30th until the 31st
- February: From the 1st until the 2nd
- March: From the 1st until the 4th, and from the 30th until the 31st
- April: From the 1st until the 2nd and from the 28th until the 30th
- May: The 1st day and the last four days of the month
- June: From the 26th until the 29th
- July: From the 25th until the 29th
- August: From the 24th until the 28th
- September: From the 23rd until the 26th
- October: From the 22nd until the 26th
- November: From the 21st until the 25th
- December: From the 21st until the 25th
Did you Know?
- People that are born under a Waning Gibbous moon are known for their reflective personality. They have an old but very wise soul, being perfect for becoming teachers, orators. The religious study can be fascinating for them.
- In the middle of autumn (7th of November in the Northern Hemisphere and the 5th of May in the Southern), the Waning Gibbous Moon appears higher than in mid-spring.
- There are four kinds of lunar months:
1.Anomalistic - 27 days, 13 hours, 18 minutes, 37.4 seconds. It's the period between one perigee and the next one.
- Nodical - 27 days, 5 hours, 5 minutes, 35.9 seconds. It is the time that it takes the Moon to pass through one node and return to it.
- Sidereal - 27 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes, 11.5 seconds. Using stars as a reference, that's how long it takes for the Moon to circle the Earth.
- Synodical - 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes, 2.7 seconds. This is the basis for most calendars we use today, and this is how we divide the year. The Moon circles the Earth in this length of time, using the Sun as reference.
Sources:
Image Sources:
- https://c.tadst.com/gfx/750w/waning-gibbous-moon.jpg?1
- https://i.redd.it/0mzx4klwcyw01.jpg
- https://www.thoughtco.com/thmb/jgfbVjZ46mEK_Sw0yezmQf4Z9h4=/3728x2796/smart/filters:no_upscale()/moon_phases-58b84a765f9b5880809d8d4d.png
- https://www.almanac.com/sites/default/files/image_nodes/moon-phases_delpixel-ss-resize2.jpg
- https://www.indastro.com/img/upload/1554189900how-to-calculate-the-moon-phase.jpg
